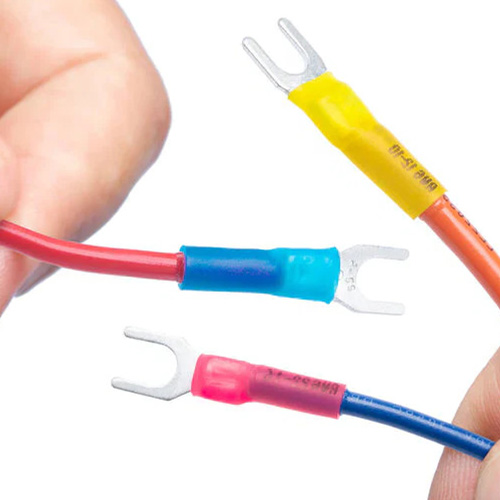
 Here’s a comprehensive guide on using heat shrink tubing for mechanical repairs. This versatile tool is essential for insulation, protection, and reinforcement in a wide variety of applications.
Here’s a comprehensive guide on using heat shrink tubing for mechanical repairs. This versatile tool is essential for insulation, protection, and reinforcement in a wide variety of applications.
What is Heat Shrink Tubing?
Heat shrink tubing is a flexible, polymer-based tube that contracts when heated, providing a snug fit around wires, cables, or mechanical components. It’s used for:
- Insulating electrical connections
- Protecting wires or cables from abrasion
- Bundling wires neatly
- Strengthening weak spots in components
- Providing strain relief
How to Use Heat Shrink Tubing for Mechanical Repairs
- Select the Right Size
Choose a heat shrink tube with a diameter roughly 25-50% larger than the component or wire you’re repairing. When heated, it will shrink to fit tightly. - Choose the Right Material
- Polyolefin: Best for general repairs, with high flexibility and durability.
- Adhesive-Lined: Provides extra sealing and moisture protection.
- PVC: Useful for less demanding applications.
- Prepare the Component
- Clean the area to remove grease, dirt, or corrosion.
- Cut the heat shrink tubing to the appropriate length, ensuring it fully covers the damaged area with some overlap on both sides.
- Position the Tubing
- Slide the tubing over the damaged or repaired area.
- If working with wires, connect or splice them before sliding the tubing into place.
- Apply Heat Evenly
- Use a heat gun, lighter, or hair dryer to apply heat evenly along the tubing.
- Keep the heat source moving to prevent burning or uneven shrinking.
- The tubing will shrink to about half its original diameter, creating a tight fit.
- Inspect the Repair
- Allow the tubing to cool.
- Check that the tubing is securely in place and provides the desired reinforcement, insulation, or protection.
Applications in Mechanical Repairs
- Cable Repairs: Repair or protect frayed electrical wires or damaged cables.
- Hose Reinforcement: Strengthen and seal small cracks or weak spots in hoses.
- Tool Handles: Add grip and insulation to worn-out handles of tools like pliers or screwdrivers.
- Thread Protection: Seal exposed threads on bolts or screws to prevent corrosion or damage.
Tips for Best Results
- Avoid overheating to prevent damage to the tubing or component.
- Use tubing with a 3:1 shrink ratio for irregularly shaped objects.
- Store heat shrink tubing in a cool, dry place to maintain its quality.

